How to Start Using a Sewing Machine: A Beginner Guide
Learn how to start using a sewing machine with a clear, step-by-step approach. Set up, thread, bobbin, stitches, and safety tips for confident beginner sewing.

You will learn how to start using a sewing machine, including setup, threading, bobbin winding, stitch selection, and basic safety. This guide covers the essential steps a beginner must master before sewing fabric, with practical tips and a simple first project.
Getting Started: Setting Up Your Sewing Machine for First Use
Before you touch fabric, create a safe, clean workspace and power up your machine. Place it on a sturdy table with good lighting, away from edges and drafts. Read the manual to understand model-specific features, then confirm the power cord and foot pedal are intact. A gentle idle test on scrap fabric helps you hear what a normal machine sounds like. According to Sewing Machine Help, the most common beginner mistakes are skipping the manual, assuming the needle is universal for all fabrics, and neglecting basic safety. Set your machine to a straight stitch first, press the foot pedal slowly, and listen for any unusual sounds. If something feels off, stop and consult the manual or a trusted video tutorial. With proper setup, you create the foundation for smooth stitching, fewer thread breaks, and consistent seams. Next, prepare to thread the upper path and wind the bobbin in the following steps.
Threading Your Sewing Machine: The Essential First Step
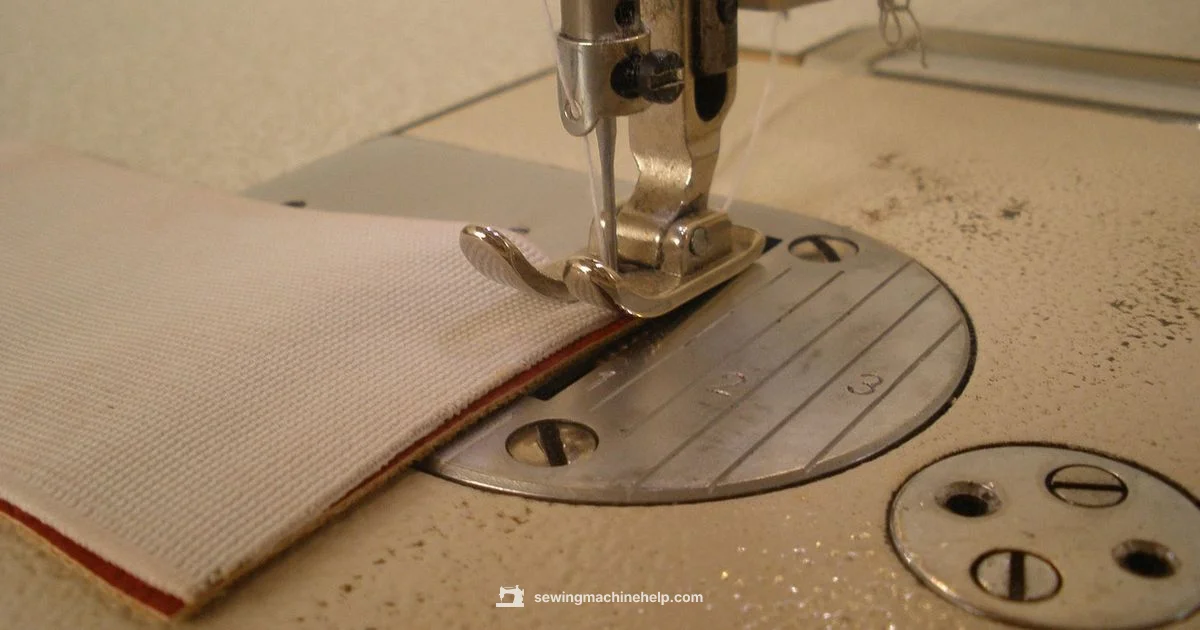
Threading is the bridge between your idea and a clean seam. Start by placing a full spool of thread on the spool pin, then guide the thread through the guides from top to bottom, finally threading the take-up lever and the needle. If your machine has a bobbin thread from below, ensure the take-up hook is engaged and the thread lies flat. Slow, deliberate threading reduces tangles and breakages. After threading, gently pull to feel the thread taut but not tight. Always consult your model’s threading diagram in the manual, as path routing can vary. Sewing Machine Help emphasizes checking for loose threads and removing lint before you sew. A quick test on scrap fabric confirms the path is correct.
Winding and Inserting the Bobbin Correctly
Winding the bobbin evenly is essential for consistent stitches. Place a fresh bobbin on the bobbin winder shaft, guide the thread through the winding groove, and press the stop to end winding when full. After winding, insert the bobbin into the bobbin case, ensuring it turns clockwise (or as specified). Place the bobbin in its housing and pull a thread tail through the slot. With the needle threaded, draw up a loop from the bobbin thread by gently lifting the presser foot and pulling the top thread. This loop pulls the bobbin thread up so you can start stitching immediately. The goal is smooth, even feeding without birds-nesting or looping under the fabric.
Thread Tension and Needle Size: Why They Matter
Tension is the gatekeeper of a clean stitch. If top tension is too tight, you’ll see puckering; if too loose, stitches may appear loose and loopy. Start with a mid-range tension setting on your machine and test on scrap fabric. Match the needle size to the fabric: universal 90/14 is a good general-purpose choice for woven cottons and similar fabrics. For lightweight fabrics, consider a smaller needle (80/12); for denim or heavy fabrics, a larger needle (100/16) works best. Always use the correct needle for the chosen fabric to prevent skipped stitches and needle breakage. Sewing Machine Help notes that needle choice can dramatically affect stitch quality and fabric damage, so pick carefully.
Loading Fabric and Selecting Your First Stitch
Begin with a straight stitch before moving to decorative options. Place a scrap of fabric under the presser foot, lower the foot, and slowly press the pedal to observe feed. Keep the edge guide aligned with the fabric edge to produce a straight seam. If your machine offers an adjustable stitch length, start around 2.5 mm for woven fabrics and adjust as needed. Practice backstitching at the beginning and end of your seam to secure threads. This builds control and reduces unraveling. Remember to reset stitch type after practice—your first project will be a simple seam on scrap material before you graduate to a real project.
Practice with Scraps: Your First Simple Project
Practice makes progress. Use fabric scraps to sew a simple straight seam 6-8 inches long, then a small zigzag to simulate finishing. Watch for thread lint and ensure the bobbin tension remains even. Short practice runs teach you how the machine responds to speed changes and stitching length. As you gain confidence, set up a small trial project like a pillowcase or napkin. The goal is to get comfortable with controlling speed, guiding fabric, and producing even stitches. Sewing Machine Help reminds beginners to celebrate small wins and revisit basics whenever you feel unsure.
Basic Maintenance and Safety Practices
Keep your machine clean and well-lubricated according to the manual. Remove lint from the bobbin area and under the feed dog after practice sessions. Use a small brush to sweep away dust, and avoid oiling unless your model requires it. Unplug the machine before any maintenance, and never place fingers near the needle while the needle is moving. Use scissors or thread snips with a stable cutting surface. Regular maintenance reduces thread jams, extends the life of your machine, and keeps your projects running smoothly.
Troubleshooting Common Start-Up Issues
If stitches skip, stop and recheck threading, bobbin placement, and needle installation. Bird-nesting under fabric often points to tension or threading errors. Ensure the needle is inserted correctly and not bent. If the machine won’t stitch, verify power and foot pedal function, and reset to the default stitch. A gentle cleaning and re-threading often resolves many issues. When in doubt, consult the manual or a reputable guide to avoid damaging your machine.
Next Steps: Expanding Skills and Tooling
As you gain confidence, explore a few beginner-friendly projects like a tote bag, pillow cover, or simple garment. Add helpful accessories such as extra feet (zipper, walking foot), a measuring gauge, and a seam ripper for corrections. Practice different stitch types and learn basic seam finishes. Regular practice builds muscle memory and speeds up your workflow. Sewing Machine Help suggests documenting your progress and noting which techniques you find most enjoyable to guide future projects.
Tools & Materials
- Sewing machine(Choose a model with reliable straight stitch and basic zigzag options)
- Power cord and foot pedal(Ensure cords are in good condition and compatible with your machine)
- User manual(Keep for model-specific guidance)
- Spool of all-purpose thread(Neutral color is easiest for practice)
- Bobbin(s)(Pre-wound or wound on the machine’s bobbin winder)
- Needles (assorted sizes)(Begin with 80/12 and 90/14 for a start)
- Scissors or thread snips(Sharp, fabric scissors preferred)
- Pins and pincushion(Keep fabric in place while sewing)
- Fabric scraps for practice(Use scrap cotton or muslin to begin)
- Measuring tape or ruler(Useful for sizing and alignment)
- Small brush or compressed air(Clean lint from bobbin area)
- Sewing machine oil (if recommended)(Only use if your manual specifies)
Steps
Estimated time: 60-90 minutes
- 1
Prepare workspace and machine
Set up on a sturdy table with good lighting. Unbox, remove any packaging, and plug in. Switch on and run a quick idle test on fabric scraps to hear normal sounds.
Tip: Check that your feet are flat and the power is stable before you start. - 2
Install presser foot and wind bobbin
Attach the appropriate presser foot for your first stitches, then wind a bobbin evenly and insert it into its housing. Ensure the bobbin threads correctly and can pull smoothly.
Tip: Wind bobbins slowly and stop when full to avoid over-winding. - 3
Thread the upper path
Guide thread from spool through guides down to the needle, ensuring the thread passes through the take-up lever. Verify the thread is seated properly in the needle’s eye.
Tip: If the thread binds or breaks, rethread with a fresh needle and check guides. - 4
Thread the bobbin and draw up
Place bobbin in its housing and pull the thread tail through until it engages with the top thread. Use the handwheel to bring up a loop from the bobbin thread.
Tip: Pull both threads to the back before starting to sew. - 5
Choose your first stitch and test
Set the machine to straight stitch on a scrap piece. Lower the presser foot and sew slowly, checking stitch length and evenness.
Tip: Backstitch at the beginning and end to lock stitches. - 6
Practice with scraps
Sew a 6–8 inch straight seam on fabric scraps to observe feed, tension, and fabric handling.
Tip: Vary speed gradually to feel how the machine responds. - 7
Move toward a simple project
transition to a small project like a pillow cover or tote bag; apply straight and basic zigzag stitches and finish edges with basic seam finishes.
Tip: Take measurements carefully and practice seam allowances.
Your Questions Answered
What should I do first when I get a sewing machine?
Unbox, read the manual, set up a stable workspace, and plug in. Do a short test stitch on scrap fabric to confirm basic function.
First, set up a stable workspace, read the manual, and test on scrap fabric to confirm basic function.
How do I thread the machine correctly?
Follow the model’s threading diagram from spool to needle, including guides and the take-up lever. Re-thread if you see knots or frequent breaks.
Follow the threading path from the spool to the needle and re-thread if you see knots.
What needle size should I use for fabric?
Choose a needle size based on fabric weight: medium-weight fabrics respond well to 90/14; lighter fabrics use 70/10 or 80/12; heavier fabrics use 100/16.
Use needle size appropriate for fabric weight, like 90/14 for medium fabrics or 100/16 for heavy denim.
How can I fix tension issues?
Check both the upper thread path and bobbin tension, ensure the needle is not bent, and test on a scrap. Adjust gradually and re-test until stitches lay flat.
Check thread path and tension, test on scrap, and adjust gradually until stitches lay flat.
Is oiling the machine necessary?
Only oil if your manual specifies it. Many modern machines are designed to run without daily lubrication. Follow the manual for exact needs.
Oil only if your manual says so; many machines don’t require daily lubrication.
What safety precautions should I follow?
Unplug before maintenance, keep fingers clear of the needle, and use scissors with care. Use a stable cutting surface and avoid distractions while sewing.
Always unplug before maintenance, keep fingers away from the needle, and sew with focus.
Watch Video
The Essentials
- Set up a stable workspace and read the manual first
- Threading and bobbin winding are the foundations of good stitches
- Match needle size to fabric for best results
- Practice on scraps before tackling real projects
- Maintain your machine to prevent issues